Origin
Colombia Telecomunicaciones S. A. E.S.P. BIC (the “Company”, Telefónica Movistar Colombia or Movistar), was incorporated in Colombia as a commercial company by Public Deed N.º 1331 of June 16, 2003 until December 31, 2092 and with its main domicile in Bogotá D.C. located at Transversal 60 N.º 114A – 55. It is subject to the legal regime set forth in Law 1341 of 2009 and other applicable regulations. Since 2021, the Company included the expression “BIC” in its corporate name, after having adopted the legal status of Collective Benefit and Interest Company.
The Company operates under the Movistar trademark. It is part of the Telefónica Group, one of the world’s leading telecommunications service providers, present in Europe and Latin America, offering telephony and mobile connectivity services, broadband services, fiber optics to the home, pay TV, fixed telephony and a complete range of digital solutions for small, medium and large companies and corporations.
Shareholding
composition
During 2024, there were no changes in the capital stock structure or other operations related to the Company’s capital.
The Company’s shareholder structure is as follows:
| Shareholder | Nit/C.C | N.º of shares | Percentage of participation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telefónica Hispanoamérica, S.A. | 900,847,726-9 | 2,301,779,819 | 67.49937427 |
| La Nación – Ministry of Finance and Public Credit | 899,999,090-2 | 1,108,269,271 | 32.49984282 |
| Radio Televisión Nacional de Colombia – RTVC | 900,002,583-6 | 10,000 | 0.00029325 |
| Shirley Puentes Mercado | 32,771,179 | 9,950 | 0.00029178 |
| Adriana Cepeda Rodríguez | 32,797,578 | 2,488 | 0.00007296 |
| Patricia Cepeda Rodríguez | 22,656,420 | 1,493 | 0.00004378 |
| Darío Cárdenas Navas | 17,066,629 | 885 | 0.00002595 |
| Eduardo Cárdenas Caballero | 19,210,431 | 826 | 0.00002422 |
| Jhon Jairo Gutiérrez Torres | 72,225,428 | 498 | 0.00001460 |
| Kira Torrente Albor | 32,732,749 | 349 | 0.00001023 |
| Canal Regional de Televisión Ltda. TEVEANDINA | 830,005,370-4 | 200 | 0.00000586 |
| Área Metropolitana de Bucaramanga | 890,210,581-8 | 2 | 0.00000006 |
| Instituto de Vivienda de Interés Social y Reforma Urbana del Municipio de Bucaramanga – INVISBU | 804,001,897-0 | 2 | 0.00000006 |
| Caja de Previsión Social Municipal de Bucaramanga | 890,204,851-7 | 2 | 0.00000006 |
| Cooperativa de Empleados de las Empresas Públicas de Bucaramanga Ltda. | 800,093,901-1 | 2 | 0.00000006 |
| Central de Inversiones S.A. – CISA | 860,042,945-5 | 1 | 0.00000003 |
| Total | 3,410,075,788 | 100.00000000% |
Our Mission
and values
Telefónica firmly believes that it is people who give meaning to technology, not the other way around. In a world where technology is increasingly present, the Company stresses that the most important connections are human, since the quality of life depends on these interactions. It is therefore engaged in providing connections that bring people together.
Telefónica is guided by core values that reflect its commitment to collaboration, innovation and trust. It fosters an open work environment, where transparency and inclusion are key to finding the best solutions. The Company defines itself as a challenger, always seeking to transform and simplify people’s lives through innovation. In addition, it is characterized by its reliability, working with honesty and commitment to offer secure and quality connections, adapting to the needs of customers throughout its history.
Strategy
Telefónica’s strategy is guided by its mission to “make the world more humane, connecting people’s lives” and its main lines of action have been revised to reflect the progress of the transformation made in recent years and its vision for the future of telecommunications. This has enabled the Company to adapt its Responsible Business Plan to the new realities of the environment.
The future of the Company is deeply linked to that of telecommunications, since digitalization is undoubtedly the path to the future. In this sense, the role of telecommunications operators is essential, and offering quality connectivity is crucial for development.

Bajo esta premisa, el Plan de Negocio de Telefónica se fundamenta en cinco pilares clave:
Sustainability of revenue growth for consumers and households: Implementing a strategy aimed at attracting and retaining customers through attractive propositions, based on the quality of its network and a product offering with integrated services that go beyond connectivity. This approach is enhanced by massive digital ecosystems and the capitalization of its national brands.
Maintaining the good momentum of the corporate business: The Company continues to expand advanced solutions for companies and the public sector, with a focus on supporting the digitalization of their businesses. Telefónica Tech is positioned as the benchmark in advanced solutions such as cloud, cybersecurity, IoT and big data, in addition to offering professional services.
Evolution of wholesale revenues and partner agreements: Telefónica seeks to generate valuable revenues by optimizing the network, providing access to different customer segments and helping to monetize infrastructure investment. The company will strengthen its wholesale business in key markets and attract software developers and integrators through the Open Gateway initiative.
Achieving operational efficiencies: Telefónica is focused on reducing its cost structure through technological transformation, accelerating the shutdown of legacy networks (such as copper, 2G and 3G) and the integration of artificial intelligence and automation to achieve greater operational efficiency.
Moderation of investment intensity: The Company maintains a differential profile while moderating investment, supported by its early commitment to fiber and 5G, as well as the completion of the main 5G spectrum auctions. This will allow it to overcome the CapEx peak and optimize network deployments through agreements with investment partners and Telefónica Infra.

- Building a greener future: Leveraging technology and digital services to achieve a holistic transition (green, social and digital) that drives a competitive and resilient economy.
- Helping society thrive: Promoting economic and social development through digitalization.
- Leading by example: Generating trust through the responsible management of its activity.
ESG management is aligned with the Company’s strategy and is consolidated in the Responsible Business Plan (RBP).
E-Environment
Building a greener futuree
- Energy and climate change
- Circular economy
- Eco Smart solutions
- Eco Rating
- ISO 14001




Social S-Social
Helping society thrive
- Connectivity and digitalization
- Gender, diversity and inclusion
- Human rights
- Ethical and sustainable products and services





Governance G-Gobernanza
Leading by example
- Corporate governance
- Ethical culture and responsible principles
- Digital trust
- Commitment to suppliers


Sustainability, both in the “what” and in the “how”, is the key to achieving the desired economic results, managing the business from a social and environmental perspective. For Telefónica, ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) management is transversal and a fundamental part of its DNA. Although from its inception in Colombia it focused on generating economic value with responsible business conduct, it was in 2021 when it formalized the adoption of the legal status of a Collective Benefit and Interest Company (BIC). This includes activities in five key dimensions: Business Model, Corporate Governance, Labor Practices, Environmental Practices and Community Practices (see chapter 15. BIC Management Report)
Movistar Planet:
Commitment to Sustainability
Movistar Planet is a portfolio of products and services designed with sustainable criteria, which integrates the commercial offer with environmental and social attributes for private and corporate customers. This portfolio promotes innovative solutions, offers training options and encourages responsible consumption.
Allies of Sustainable
Development in Colombia
Based on its Responsible Business Plan, centered on the three fundamental axes: Building a greener future, Helping society thrive, and Leading by example, the Company contributes significantly to the goals of the 2030 Agenda as follows:
Building a greener future
To increase the contribution to society and the environment for a more sustainable and respectful development of the planet.


To have a more efficient telecommunications network powered by renewable energy.

Provider of digital solutions that help customers reduce their CO2 emissions and drive Sustainable Mobility.

Promote the circular economy and responsible consumption in the use of electronic devices through reuse and recycling.
Helping society thrive
Promote inclusive connectivity that brings digitalization closer to all people, favoring the social and economic development of the communities in which it operates.

To provide faster and better quality Internet to individuals and businesses.


To manage talent by promoting labor equity, the inclusion of people with disabilities, and the promotion of digital talent aligned with the economy of the future.


Address inequalities by investing in education, digital skills and accessibility with a differential offer.
Leading by example
Generating trust through actions and commitments, and ensuring digital trust and the promotion of sustainability among all stakeholders.

Improving trust through ethical and responsible use of technology, robust corporate governance and ensuring that the security and privacy of customer data is safeguarded.

Commitment to the highest standards of business principles and ethics, promoting sustainability in the supply chain.
As a leader in the Information and Communications Technology (ICT) sector, Telefónica Movistar Colombia is actively committed to contributing to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
While SDG 9 (building resilient infrastructure, promoting sustainable industrialization and fostering innovation) is the one most directly influenced by the Company, it also has a positive impact on other key SDGs, such as those related to economic growth and equal opportunities (SDG 4, SDG 5, SDG 8 and SDG 10), environmental protection (SDG 7, SDG 12 and SDG 13), quality education (SDG 4), the development of sustainable societies (SDG 11), the promotion of ethical behavior and integrity (SDG 16), and the generation of partnerships for the fulfillment of these goals (SDG 17). Movistar continues to work on integrating these SDGs into its operations and strategies, contributing to sustainable development and improving the quality of life in the communities where it operates.
Movistar Colombia
in Figures
Movistar Colombia is one of the major drivers of the digital economy in the country.
Its main figures are:

Employment
Direct:
5,422**
InIndirect
(Partners and Commercial Agents):
17,718
Customer accesses
24.4
million
Mobile: 20,772,360
Landline: 1,202,944
Broadband: 1,548,706
TV: 848,550
Operating income
COP 6.672 Billion
EBITDA*
COP 1.547 Billion
Figures in Colombian pesos (COP).
** Direct and temporary jobs. Does not include Fundación Telefónica Movistar payroll.
Business Model and
Value Chain
The telecommunications business is based on the investment and operation of a series of assets, mainly network assets, to offer connectivity services to all its customers.
The Company’s traditional value chain includes the following elements:
- Assets
tangible and intangible elements resulting from a normally capital-intensive investment. They are mainly fixed and mobile networks owned by the company or third parties, their subsequent evolutions, business and service platforms and other intangible elements (licenses, spectrum, brands, etc.) and digital platforms (data centers, hardware and software).
- Services
companies in the sector develop their own services based on their own or third-party deployed assets. The Core business includes the main fixed and mobile communications businesses, although operators have been evolving towards businesses adjacent to connectivity and customer service through different channels, including experience centers.

- Customers
integrated telecommunications companies, such as Telefónica, usually have a very diverse portfolio of customers in each of their markets (residential, corporate and public administration segments, among others). The commercial offer is tailored to meet their needs.
However, networks are evolving towards models similar to software platforms, giving rise to new business models based on making the main capabilities of networks available through connections or applications to various players (not only end customers). This is the birth of digital services: cybersecurity, cloud, internet of things (IoT), big data and advertising.
Assets
- Physical Assets:
- Fixed Networks
- Mobile Networks
- IT (Datacenters & Hardware)
- Real Estate
- Intangible Assets:
- IT Platform (Software)
- Operations and Processes
- Licenses and Spectrum
Services
- Basic Telecommunications:
- Connectivity
- Communications
- Digital Services:
- TV and Content
- Cloud Services
- loT
- Etc
- Professional Services:
- Security
- Big Data
- Managed IT Services
- Etc
Customers
- Residential:
- Households
- Individuals
- SMEs, Businesses, and Professionals
- Large Corporations
- Multinationals
- Public Administrations and Entities
Products and Services
Telefónica Movistar Colombia offers a broad portfolio of products and services for the connectivity and digital transformation of individuals, entrepreneurs, SMEs, businesses and corporations (see more in chapter 5.3. Digital Solutions for Companies).
Mobile products and services
Prepaid
Postpaid
Terminals
Fixed services
Broadband internet
(Fiber/Copper)
Television
Fixed telephony
Digital services
Internet of things (IoT)
Big Data
Advertising
Cyber security
Cloud
| Customer Plant/Accesses | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mobile | Basic line | Broadband | Television | Dedicated | RPVS | Total | ||||
| Prepaid | Postpaid | FTTH | Copper | |||||||
| 15,638,053 | 5,134,307 | 1,202,944 | 1,491,315 | 57,391 | 848,550 | 6,460 | 11,682 | 24,390,702 | ||
Participation
in Initiatives
In order to strive for sustainable development, the Company promotes and participates in several initiatives in coordination with national and international organizations:

- Early Adopter, Anti-Corruption Roundtable, Inclusion Roundtable, WEPs – Women’s Empowerment Principles, Human Rights Roundtable of the Global Compact Colombia Network.
- Agreement for Sustainability – Andesco.
- Unicef’s #TratameAlDerecho (Treat Me Right) campaign (promoting the elimination of violence against children and adolescents).
- Safe Workplaces Without Harassment (ELSA) – GenderLab and Inter-American Development Bank.
- Colombia Guides on Human Rights (HR) and International Humanitarian Law (IHL).
- United for the SDGs Alliance.
- Viguías – Safe Internet Center (I Protect You, You Lead, I Guide You and Knowledge Center).
- Corporate Commitment Against Corruption (CEA) – Transparencia por Colombia.
- Responsible Business Conduct Committee (CER) – Bogota Chamber of Commerce.
- De Empresas Para Empresas (DEPE) – Alliance for Integrity and Global Compact.
- EcoCómputo- Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) Management
- Safe Spaces – Office of the Mayor of Bogotá D.C.
- G12 – Grupo Éxito, Bavaria, ISA, Postobón, Enel, Ecopetrol, Terpel, Grupo Sura, Grupo Nutresa, Grupo Argos, Grupo Bancolombia.
- Internet Governance Board for Colombia.
- My Game My Name, an international initiative to report sexist treatment in the gaming industry.
- Pride Connection Colombia (LGBT+ Community).
- Vision 30/30 Packaging Management.
- We Take Action – Alliance for Integrity.
- ESG Sustainable and Responsible Business Commission – Spanish-Colombian Chamber of Commerce.
Associations
Telefónica Movistar Colombia participates in the following guilds and associations:

Association of the Colombian Mobile Industry – ASOMOVIL
Interamerican Association of Telecommunications Companies – ASIET
National Association of Businessmen of Colombia – ANDI
National Association of Businessmen of Colombia – ANDESCO
Association for the Advancement of Management – APD
Official Chamber of Commerce of Spain in Colombia CAMACOES
Colombian Chamber of Electronic Commerce
Bogotá Chamber of Commerce Affiliates Circle
Center for Research and Development in Information and Communication Technologies – CINTEL
Excellence in Justice Corporation – CEJ
Global Compact Local Network Corporation in Colombia
Carolina
Foundation
Colombia Guides on Human Rights and Businesses
PROBOYACÁ
Liberator Region
Recognitions, Awards
and Rankings
Equipares Gold Seal from the Ministry of Labor and the United Nations Program UNDP: Movistar is the first Telco in Colombia to receive the recertification.
Ranked 1st
Speedtest Award de Ookla, as the Operator with the fastest fixed Internet in Colombia for the sixth consecutive time.
Ranked 4th
in the 100 Open Startups in partnership with Connect: Wayra as one of the companies that most supports entrepreneurship in Colombia.
Ranked 1st
in the Telco Sector and 4th overall in the Top 10 Open Corps Ranking for Open Innovation and Entrepreneur Engagement
Ranked 2nd
Most Innovative Company and 8th Most Innovative CEO Fabián Hernández in the Change Markers Colombia – Horse Ranking
Andesco Sustainability 2024 Award in the Gender Equity category for the Women in Network Program
Mujeres en Red (Connected Women) as a pioneer initiative in the Latam Inclusive Tech Awards
Ranked 10th
in the ranking of Companies Committed to Youth in Ibero-America by the International Youth Organization – OIJ.
Best Bicycle Use Promotion Program delivered by the District Mobility Secretariat and its network Muévete Mejor: bicycle and scooter sharing system.
Quality Seal for the bike parking spot at the Morato location, awarded by the District Mobility Secretariat and its Muévete Mejor network.
MERCO Companies (2024): Corporate Reputation Business Monitor: Telco Sector Ranked 2nd, and 60th in Total companies
MERCO Talent (2024): Telco Sector Ranked 1st, and 60th in Total companies
MERCO ESG Responsibility (2023): Telco Sector Ranked 2nd, and 71st in Total companies
Best Telework Program delivered by the District Mobility Secretariat and its network Muévete Mejor: promoting flexibility and balance between personal and professional life.
Certified Management
Telefónica Movistar Colombia has an Integrated Management System structured under the ISO standards.
The Integrated Management System is made up of:

The Quality Management System (QMS), certified since 2007 and structured under the ISO 9001 standard, seeks to control and improve its performance, as well as efficiency and excellence in the services provided.

The Environmental Management System (EMS), certified since 2007 and structured under the ISO 14001 standard, seeks to protect the environment and respond to changing environmental conditions, in balance with socioeconomic needs.

The Occupational Health and Safety Management System (SGSST) certified since 2015 and structured under the ISO 45001 standard, which seeks to manage and control the risks associated with the safety and health of workers.

The Information Security Management System (ISMS), certified since 2016 and structured under ISO 27001, which seeks to preserve the basic properties of information.

The Anti-Bribery Management System (ABMS) certified since 2022, structured under the ISO 37001 standard, which seeks to avoid or mitigate the costs, risks and damages of engaging in bribery and acts of corruption.

The Business Continuity Management System (BCMS) certified since 2022 structured under ISO 22301, which seeks to prepare, provide and maintain plans, procedures and capabilities to continue operating during disruptive events.
The Integrated Management System is a tool to support sustained compliance with the needs and expectations of stakeholders. At least once a year, senior management reviews the performance of each Management System to ensure its suitability, adequacy and effectiveness and to make decisions regarding improvement actions, resources or any required changes.
Each year internal audits for the Integrated Management System are contemplated as an essential activity to make sure management objectives are followed, evaluate and ensure compliance with procedures, policies and controls, and their effectiveness. Similarly, an external audit evaluation is performed for each section of the standards according to the scope of the IMS, which includes Each year internal audits for the Integrated Management System are contemplated as an essential activity to make sure management objectives are followed, evaluate and ensure compliance with procedures, policies and controls, and their effectiveness. Similarly, an external audit evaluation is performed for each section of the standards according to the scope of the IMS, which includes indicators, legal requirements, risks, among others, to determine whether the Management System is in line with the needs of the operation and with the criteria defined by the international standard established for each system.

For the year 2024, 41 audits were conducted nationwide, in order to identify timely improvements to the Management Systems, both internal and with third parties (suppliers), ensuring the planning of actions and strategies aimed at solving the identified deviations, as well as the execution of 7 auditing exercises by the External Certification Body, where satisfactory results were obtained, ratifying the certification under international standards, proving an adequate degree of maturity, which continuously improves and leverages on the organization’s strengths.
Likewise, the Management Systems analyze the needs and expectations of interested parties based on the dialogues and materiality analysis conducted by the Sustainability team. Within these material issues, it has been identified that stakeholders value various aspects related to the scope of the Company’s Management Systems, such as, for example:
For these material issues, action plans are defined with the objective of improving the level of stakeholder appreciation.
- Responsible marketing
- Customer promise
- Digital security
- Responsible supply chain management
- Ethical behavior and corporate governance
- Contribution to the fight against climate change
- Circular economy
- Employee welfare

Risk Management
Model
Telefónica has a Risk Management Model based on COSO ERM 2017 (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission). It is implemented in Colombia Telecomunicaciones, and those responsible for the Company, in its scope of action, carry out the timely identification, evaluation, response and monitoring of the main risks.
This model, inspired by best practices, facilitates the prioritization and development of coordinated actions to address risks, both from a global perspective for the Group and specifically in Colombia.
On the other hand, the Responsible Business Principles specifically state that: “We establish adequate controls to evaluate and manage all relevant risks for the Company”. In this sense, the Company has a Risk Management Policy, approved by the Board of Directors, and a Corporate Risk Management Procedure for the Telefónica Group, both based on experience, best practices and Good Corporate Governance recommendations, thus contributing to continuous improvement in business performance.
El Modelo se adapta a los cambios del entorno y analiza periódicamente el contexto interno y externo de la CompaThe Model adapts to changes in the environment and periodically analyzes the Company’s internal and external context.ñía.
As a result, and in order to facilitate the risk identification process for the Company’s managers, the Telefónica Group has a risk catalog that is updated periodically , which allows to homogenize and consolidate the information and to meet the requirements of internal and external reporting on the main risks.
This catalog considers four categories:
- Business Risks – related to the industry and especially to the Company’s strategy, such as competitive developments and market consolidation, regulatory framework, supply chain, technological innovation, data privacy, talent management, adaptation to changing customer demands and/or the development of new ethical or social standards.
- Operational Risks – related to cybersecurity; climate change, natural disasters and other factors that may cause physical damage to the technical infrastructure that may cause network failures, service interruptions or loss of quality; customer-related risks; people-related risks, as well as operational management.
- Financial Risks – arising from adverse movements in the economic environment or financial variables, and the Company’s ability to meet its commitments, liquidate its assets and have the financing capacity to carry out the business plan, including tax issues.
- Legal and Compliance Risks – related to litigation and regulatory compliance, including anti-corruption legislation, as well as compliance with legal obligations and the Company’s own environmental, social and governance (ESG) objectives including climate.
Risk
Management Process
The risk management process takes the Company’s strategy and objectives as the basis for identifying the main risks that could affect their achievement. Risks are identified and evaluated by managers in order to prioritize their reporting and follow-up, but especially to determine the response to them, mainly through mitigation plans, or strategies to avoid or transfer such risks. In general, risks are updated at least every six months, in addition to emergency or exceptional reports for new ones, or significant changes that are considered relevant.
The process consists of four stages, described below:
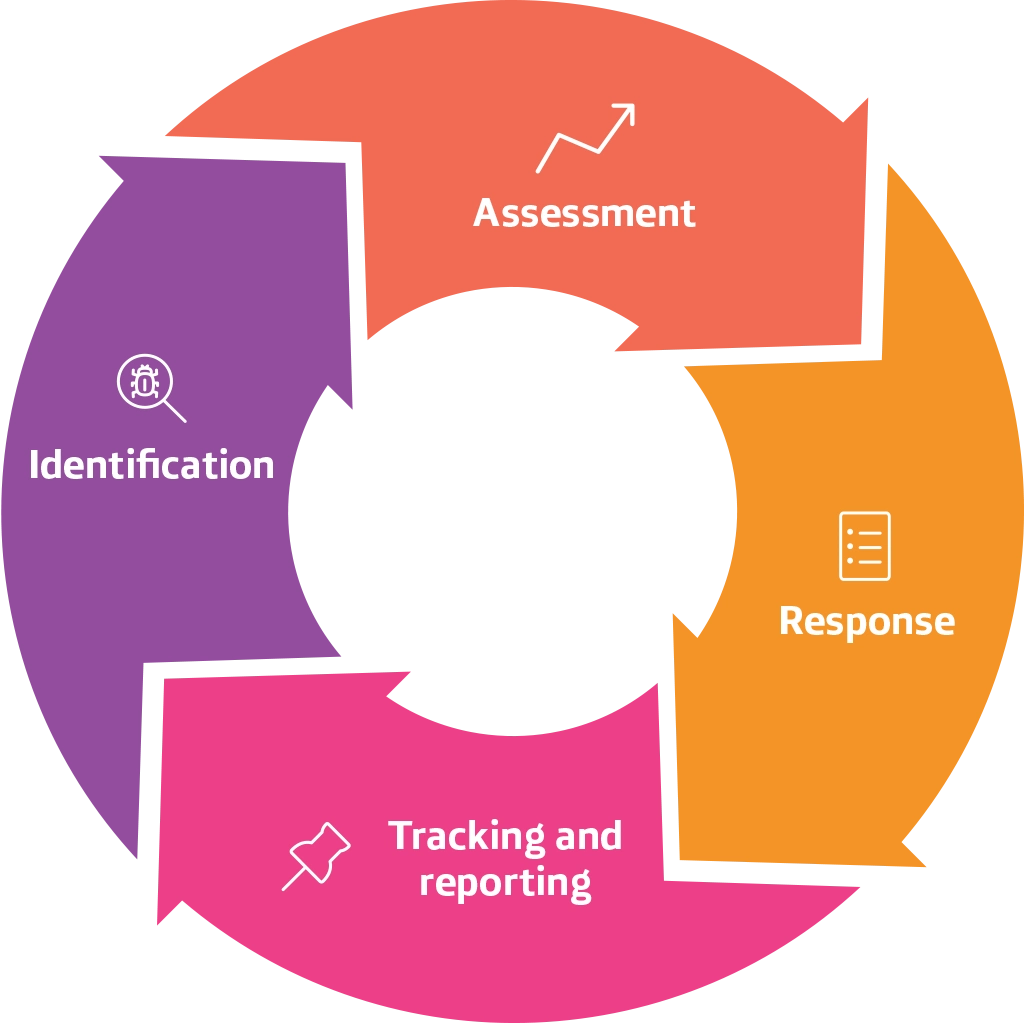

Identification
Risks are identified by management on the basis of both the factors that cause them and the effects they may have on the achievement of objectives. This identification considers both those associated with the strategic plan and potential ‘emerging’ ones, meaning risks that could eventually have an adverse impact on future performance, although their outcome and time horizon is uncertain and difficult to predict.
Assessment
This stage aims to give an order of magnitude or relevance of the risks, considering both their possible impact and their probability of occurrence.
Tracking and reporting
In accordance with the diverse typology of risks, the mechanisms for monitoring and responding to them include global initiatives and/or actions specifically aimed at addressing specific risks in Colombia.
Response and action plans
The Risk Management Model contemplates both the identification and evaluation of risks and the establishment of reasonable response and follow-up mechanisms. In this sense, it contemplates procedures to respond to challenges.
Certain risks may be fully or partially insured through the insurance market or through the Telefónica Group’s instrumental insurance subsidiaries.
The Telefónica Group is constantly insuring risks through insurance policies.
Mitigate
Take measures to reduce the probability of occurrence of the risk or its impact.
Avoid
Change the way of acting or not proceeding with the activity that causes the risk.
Accept
Make the decision to assume a risk based on management criteria, and justify the reason for such decision.
Transfer
To a third party through the contracting of insurance or outsourcing of activities.
Roles and
Responsibilities
Everyone within the organization has a responsibility to contribute to risk management, which entails integrating this concept and describing each person’s duties. In order to coordinate these activities, the following roles and responsibilities are distributed:

- Risk management function:
as a support to the development of supervision activities by the Audit Committee, a risk management function has been established within the Internal Audit area, independent from management, in order to promote, support, coordinate and verify the application of the provisions of the Risk Management Policy. This function is not the owner of the risks, nor does it assume responsibility for actions taken against them, a mission entrusted to the areas responsible for the risks.
- Risk managers:
they actively participate in the risk strategy and risk management decisions. Each of the risks identified will be assigned a manager (normally a senior manager), who will prepare a plan for their mitigation and effectively monitor their evolution.
- Supervision of the risk management system:
the Board of Directors, through its Audit Committee, supervises the efficiency of the Risk Management System.

Main Impacts, Risks
and Opportunities
The most significant risks and uncertainties facing the Company that could affect its business, financial position and results of operations should be considered together with the information contained in the financial statements:
- The Company operates in a highly regulated market; therefore, unfavorable changes in regulatory conditions could significantly affect the competitive scenario faced.
- The growing sophistication and automation of cybercrime, together with technical vulnerabilities present in systems or networks, could generate possible information leaks, unauthorized access or unavailability of systems, as well as contingencies for non-compliance with local regulations and reputational impact in the event of media accusations.
- The Company operates in highly competitive markets and therefore faces the challenge of marketing products and services efficiently and reacting adequately to the different commercial actions carried out by the different competitors.
- The Company is exposed to litigation of various types, the results of which are unpredictable and may affect it, not only in economic terms, but also because of their impact on its image and reputation due to their possible repercussion in the media.

Stakeholder participation allows the Company to understand the context in which it operates, as well as to identify both strengths and opportunities for improvement in which it must define its action plans.
Relationship with
Stakeholders
and Materiality
The Company is interested in building relationships of trust with its stakeholders. According to the mapping carried out by the Stakeholder Panel consultation, seven key categories are defined:
I.
Customers:
both residential (B2C) and business (B2B) customers, as well as all organizations representing customers.
II.
Employees:
employees, associations and unions representing workers’ interests.
III.
Strategic partners and suppliers:
key companies for the development and provision of services, as well as supplier companies and agencies and associations representing supply chain interests.
IV.
Shareholders and investors:
companies that invest in Colombia Telecomunicaciones and/or analyze its sustainable profitability.
V.
Government entities and regulators:
local, national and international organizations.
VI.
Opinion leaders, media and communication services:
influencers, press, communication agencies, branding and advertising.
VII.
Society:
(including communities, NGOs, sustainability-Eastd organizations, business and advisory associations): affected communities, as well as special groups, NGOs, companies, think tanks, business schools and universities.
Algunos de los canales de diálogo usados son:
Stakeholder Panel
Responsible Business Channel
eNPS measurement
Dialogues/ Cafés
Workplace, intranet
Social networks
Questions, Complaints and Claims Channels (PQR)
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Shareholder Service Office
Labor Coexistence Committee
Diversity Committee
Joint Occupational Safety and Health Committee (Copasst)

Through the stakeholders, the context in which the Company operates is understood, as well as identifying both the strengths and opportunities for improvement in which it must define its action plans.
In addition to this, the Company knows the perception of its stakeholders and maintains a relationship with them through dialogue tools and channels, some actions by stakeholders are:

Collaborators
- Workplace wellness: Implementation of programs such as Conecta Vida and the Digital Disconnection campaign to balance work and personal life.
- Inspirational Leadership: Initiatives such as Master Leader, Conversation Circles, and specific guides to empower leaders.
- Recognition: Significant increase in recognition among employees (+250 %) through campaigns such as Gente de Valor and Hispam Reconoce.
- Authentic connections: Spaces such as inspiring encounters and team-building activities.
- Communication and awareness: Campaigns to promote understanding and commitment to eNPS.
- 15 discussion forums led by the chief executive officer at the national headquarters, and 145 led by regional directors and managers.
- Regional Connection: monthly communication format on the Company’s progress and results with chapters dedicated to the regions to highlight their contribution and relevance in achieving the business objectives.
- Management meetings: Hybrid quarterly meetings (workplace and face-to-face) to review key operating and financial indicators and receive perspectives from external expert guests to learn their views on the contribution of technology to development and the role of innovation for economic and social transformation. An average of 1,300 employees participated, and a cascading communication strategy ensured effective
Shareholders and Investors
The Company has both the Shareholder Service Office and the Investor Service Office. In 2024, in addition to the meetings of the General Shareholders’ Meeting, two bulletins were issued to shareholders informing them of the main events related to the Company, the financial statements at the end of the year and interim periods, as well as the progress of the Responsible Business Plan. Similarly, in the case of investors, 127 requests were received from 60 investors, responding by mail or scheduled meeting.

Media/Journalists
The Company implemented several strategic initiatives to strengthen its relationship with the media and journalists, including the following:
- Media Management: The main media topic of the year was the non-binding agreement between Telefónica Colombia and Millicom to explore the combination of their operations, for which explanatory interviews were conducted. Also, other issues such as the decision of the International Center for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID) in favor of Telefónica and the termination as suppliers of SENA.
- Cybersecurity training: In response to the hacking of more than 100 journalists in 2023, 8 face-to-face and virtual trainings were carried out in collaboration with Telefónica Tech and Movistar Empresas. These impacted 125 journalists from 30 media outlets and achieved the participation of 1,200 people in the first training aimed at parents.
- Launch of the “Plan Periodista” (Journalist Plan): More than 120 journalists were presented with an exclusive 10% discount on postpaid plans and fiber optics, consolidating the company as the first telecommunications operator in Colombia to offer this benefit.
- Sector interviews: 226 interviews were conducted to help journalists understand regulatory issues, such as the mobile network unification with Tigo, and the challenges of the Telco sector in the country.
- Gaming and female inclusion: Led two events on the participation of women in eSports, including the Women in eSports Level Up, with more than 1,250 attendees and extensive media coverage.
These actions strengthened the relationship with the media, promoted understanding of the sector and consolidated the Company’s image as a leader in innovation and social commitment.
Digital Relationship
In 2024, Telefónica and Movistar stood out significantly in the digital environment. Mentions of these brands reached 802,615 interactions, impacting 467.4 million profiles. Of these, 54 % reflected positive sentiment, 30 % neutral and 16 % negative.
Main drivers of positive mentions:
- Sponsorships: Movistar Arena, with weekly ticket raffles, was the biggest generator of positive mentions..
- Sports initiatives: Digital activities such as Movistar GameClub, dynamics with the Colombia National Team, and cycling events under the hashtag #RetoMovistar.
Outstanding Institutional Campaigns: These included milestones such as Telefónica’s Centennial, the launch of the 5G network, Cooper Skin, the awarding of the MACC Movistar 2024 Women of Excellence Scholarship, and the Meeting for Digital Inclusion.
These actions consolidated the Company’s digital presence, generating positive connections with diverse audiences and strengthening the positioning of its brands.
Customers
Customers seek efficient solutions in every interaction with the Company, preferably at the first contact. Their main concerns are grouped in two areas: service performance and value proposition.
In terms of operation, they expect stability and rapid resolution of interruptions, although external factors such as vandalism, theft and public works may affect Movistar’s network. Regarding the value proposition (offer, price and plans), their concerns are focused on tariff variations, fulfillment of offers and competitiveness vis-à-vis other companies.
To evaluate customer experience, Telefónica uses the Net Promoter Score (NPS). This system, applied globally, allows us to compare operations in different regions through random surveys managed by an external firm, guaranteeing objectivity and quality in the results. In 2024, 42,480 surveys were conducted with an Estimated Error (EE) of 0.06, ensuring the reliability of the data.
The results prompted the company to optimize processes, policies and platforms that impacted the customer experience. A plan was implemented with structural initiatives monitored weekly by the executive committee and multidisciplinary teams were created to analyze root causes and solutions. These actions involved authorities, suppliers and industry best practices, with support from Telefónica’s global and regional teams.
Satisfaction analysis is complemented by transactional surveys, which allow for a quick response to any negative impact. In 2024, a total of 4,152,849 surveys were conducted, with a monthly average of 346,071. We were able to stabilize and automate 100% of the measurement of processes, extending its scope to all areas of the Company for comprehensive monitoring. In terms of indicators, there were significant year-on-year improvements: an increase of +10 percentage points in the renewal and replacement experience, and an improvement of +16 pp in technical support in the field.

Materiality
To update the material topics, the Company follows the recommendations of the GRI Standards through a four-step process:
Context analysis
Identification of actual and potential impacts
Evaluation of importance and performance
Prioritization of the most significant impacts
1.
Context analysis:
This includes the monitoring of media, social networks, guilds, control entities, competition and legislative agenda, in addition to the mission, portfolio of products and services, sector analysis, value chain, sustainability context and BIC companies, together with the identification of the Stakeholders.
2.
Identification of actual and potential impacts:
Based on the EY study (2020) on contribution to human development, the Integrated Management System and the analysis of contributions to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
3.
Materiality and performance assessment:
Through the consulting firm Ipsos, a Materiality Assessment (2023) was conducted to identify relevant aspects that impact stakeholders and the business model. This process included consultations with key stakeholders in 8 Hispam markets (with 807 surveys in Colombia out of a total of 3,477). It remains in force in 2024.
4.
Prioritization of significant impacts:
Issues are ranked in a matrix that crosses importance with perceived performance, focusing management on the most relevant aspects with the lowest identified performance.

This approach allows us to strategically allocate resources and manage the most critical issues for the Company’s sustainability and performance.
The management of the Company’s Material Issues is discussed in the chapters of this Report.
Material Issues
The Company’s Materiality Matrix organizes material issues along two main axes: importance (to stakeholders) and performance (perceived by the organization). The issues are grouped into seven key dimensions covering 18 main variables.

| Dimension | Definition | Issues |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Relationship | Aspects related to service, attention, quality and safety of products and services. |
|
| Human Capital Management | It includes talent, diversity, organizational culture and employee well-being. |
|
| Relationship with Partners and Suppliers | Commitment to sustainability in the value chain and long-term relationships. |
|
| Business Ethics and Corporate Governance | Ethical practices, regulatory compliance, transparency and emergency response. |
|
| Connecting Society as a Whole | Guarantee access, continuity and responsible use of technology for social development. |
|
| Climate Change and Environment | Minimization of environmental impact and promotion of the circular economy and biodiversity. |
|
| Impact on Society | Contribution to socioeconomic development, employment, social action and public health. |
|

Materiality Matrix



